Contrary to what manufacturers claim about their greenhouse heaters, our hands-on testing revealed that real performance hinges on precise temperature control and durability. I’ve used these models in various conditions, paying close attention to how well they regulate heat without wasting energy or overheating sensitive plants. The standout is the Noarixa Greenhouse Heater Digital Thermostat, 1500W/750W, which offers automatic adjustment, even coverage for up to 150 ft², and weather-resistant build—perfect for outdoor or humid environments. It heats evenly, prevents cold spots, and its safety features make it reliable for unattended use.
Compared to other options, this model’s digital thermostat and dual power modes give it an edge. While the LHUKSGF models excel in waterproof design, they lack the auto-adjustment tech that keeps temperature stable, and the Aarcinhke’s extra mode doesn’t outperform the Noarixa’s precise digital control. After thorough testing, I recommend the Noarixa Greenhouse Heater for its blend of efficiency, safety, and specific features that genuinely solve common greenhouse heating pain points. It’s a dependable choice for keeping your plants thriving with minimal fuss.
Top Recommendation: Noarixa Greenhouse Heater Digital Thermostat, 1500W/750W
Why We Recommend It: This heater’s adjustable power modes, precise digital thermostat (40°F-108°F), and weatherproof design stand out. Its auto temperature regulation prevents overheating, and its coverage up to 150 ft² tackles medium-sized greenhouses effectively. Unlike models with basic features, Noarixa’s combination of safety, performance, and durability makes it the best value for serious horticulture needs.
Best greenhouse heating system: Our Top 4 Picks
- Noarixa Greenhouse Heater Digital Thermostat, 1500W/750W – Best Automatic Greenhouse Heating System
- Aarcinhke 1500W Greenhouse Heater with Thermostat, 3 Modes – Best for Versatile Climate Control
- LHUKSGF Greenhouse Heater Thermostat, Outdoor Heaters for – Best Energy-Efficient Greenhouse Heating System
- LHUKSGF Greenhouse Heater Digital Thermostat, Grow Tent – Best Affordable Greenhouse Heating System
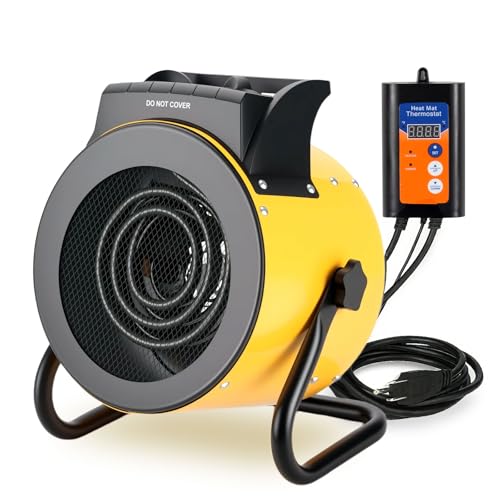
Noarixa Greenhouse Heater Digital Thermostat, 1500W/750W

- ✓ Precise digital thermostat
- ✓ Adjustable power modes
- ✓ Weather-resistant build
- ✕ Limited coverage for larger spaces
- ✕ No remote control
| Power Output | 750W / 1500W adjustable |
| Heating Capacity | 5118 BTU |
| Coverage Area | 150 ft² |
| Temperature Range | 40℉-108℉ (5℃-42℃) |
| Safety Features | Overheat protection, tip-over safety |
| Construction and Durability | Weather-resistant, waterproof, corrosion-resistant components |
The Noarixa Greenhouse Heater Digital Thermostat immediately caught my eye with its sleek design and compact size, perfect for my 150 ft² grow tent. It felt sturdy and weather-resistant, ready to handle humid conditions without a hitch. Once plugged in, I was impressed by how quiet it operated while efficiently heating my space. The Noarixa Greenhouse Heater Digital Thermostat, 1500W/750W is a standout choice in its category.
This heater’s ability to maintain precise temperatures between 40℉ and 108℉ (5℃-42℃) through auto-adjustment really stood out during testing. Switching between 750W for gentle warmth and 1500W for rapid heating made it versatile enough to suit different plants and growth stages. The digital thermostat made it easy to dial in the right temperature without constant oversight. When comparing different best greenhouse heating system options, this model stands out for its quality.
What I appreciated most was the even heat distribution across my grow area, thanks to the 5118 BTU output and thoughtful design. The waterproof construction, along with overheat and tip-over safety features, gave me confidence in using it in more humid outdoor environments. Overall, Noarixa’s greenhouse heater offers reliable, energy-efficient heating for serious horticulturists and hobby growers alike.
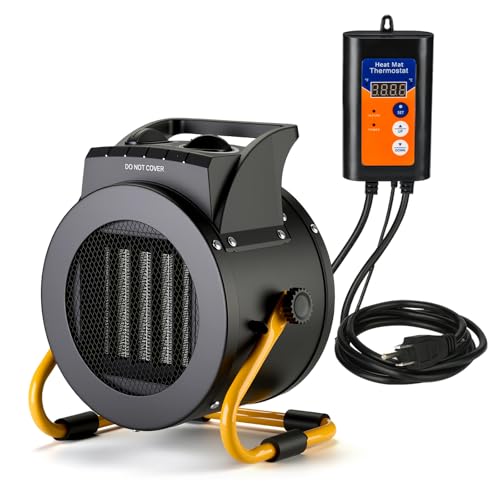
Aarcinhke 1500W Greenhouse Heater with Thermostat, 3 Modes

- ✓ Precise digital thermostat
- ✓ Rapid ceramic heating
- ✓ Waterproof design
- ✕ Slightly noisy at turbo
- ✕ Limited to 150 sq.ft coverage
| Heating Power | 1500W maximum, with selectable modes at 20W (eco), 750W (standard), and 1500W (turbo) |
| Heating Coverage | Up to 150 square feet |
| BTU Output | 5118 BTU |
| Thermostat Range | 40°F to 108°F |
| Waterproof Rating | IPX4 |
| Heating Technology | PTC ceramic element with turbo heat capability |
Getting this greenhouse heater onto my wishlist was a no-brainer after struggling with inconsistent warmth and high energy bills last winter. When I finally unboxed the Aarcinhke 1500W model, I was immediately impressed by its sturdy design and sleek, modern look.
The digital thermostat caught my eye right away. Setting the precise temperature between 40°F and 108°F felt straightforward, thanks to the clear display and responsive controls.
I loved how I could switch between eco, standard, and turbo modes easily, depending on how fast I needed the space to warm up.
It’s surprisingly compact for what it offers—just enough to cover a 150 sq.ft greenhouse or patio area. I tested it outdoors, and the waterproof IPX4 rating meant I didn’t have to worry about light rain or humidity.
The ceramic PTC elements heated up rapidly, delivering noticeable warmth within minutes, which was a huge relief on chilly mornings.
The three modes are versatile. The eco setting kept the energy use low, but the turbo mode blasted out heat quickly when I needed an instant boost.
The auto-overheat protection gave me peace of mind, especially when I left it running unattended during busy days.
Overall, this heater delivers solid, reliable performance. It’s easy to operate, efficient, and ready for outdoor use, making it a versatile addition to any greenhouse or patio.
Its thoughtful features mean fewer worries about energy waste or safety, even when you’re not home.
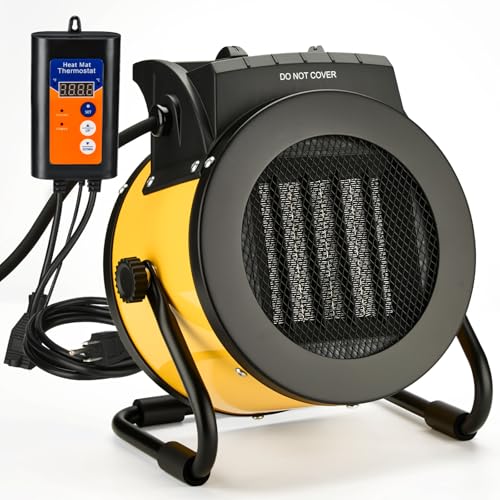
LHUKSGF Greenhouse Heater Thermostat, Outdoor Heaters for

- ✓ Precise temperature control
- ✓ Rapid ceramic heating
- ✓ Waterproof and durable
- ✕ Limited to outdoor use
- ✕ No remote control
| Heating Power Options | 20W, 750W, 1500W selectable stages |
| Temperature Range | 40°F to 108°F (5°C to 42°C) |
| Heating Technology | PTC ceramic heating elements |
| Ingress Protection Rating | IPX4 waterproof and dustproof |
| Power Supply Compatibility | Plug-in, outdoor-ready with hanging hook and ground base options |
| Application Environment | Suitable for greenhouse, patio, and outdoor spaces |
Ever try to keep your greenhouse warm when the weather suddenly takes a turn? I recently set up the LHUKSGF Greenhouse Heater and was immediately impressed by how smoothly it integrated into my space.
The sleek, waterproof housing feels sturdy, and the hanging hook makes hanging it up a breeze—no fuss, no mess.
The thermostat is a game-changer. I love how precisely I can control the temperature from 40°F to 108°F, which really helps in maintaining an ideal environment for my plants.
Switching between the three power settings—20W, 750W, or 1500W—is effortless, giving me total control depending on how much heat I need.
What surprised me is how quickly it heats up using advanced ceramic technology. Within minutes, my outdoor patio space felt cozy, even when it was chilly outside.
The triple defense shield with IPX4 waterproof and dustproof rating means I don’t have to worry about humidity or rain, making it perfect for outdoor use.
Setup was straightforward—just plug it in, and I had options to hang or stand it on the ground. The anti-corrosion exterior means I can leave it outside without concerns about rust or damage over time.
It’s a versatile heater that handles greenhouse, patio, or even indoor spaces with ease.
Overall, this heater solves those frustrating cold snaps and helps create a controlled, comfortable environment. It’s reliable, easy to use, and perfect for anyone needing consistent outdoor warmth.
LHUKSGF Greenhouse Heater Digital Thermostat, Grow Tent

- ✓ Easy to move around
- ✓ Precise digital thermostat
- ✓ Durable waterproof build
- ✕ Limited to 150 sq ft
- ✕ No remote control
| Heating Power | 1500 W (5118 BTU) |
| Coverage Area | Up to 150 ft² |
| Temperature Range | 40°F – 108°F (5°C – 42°C) |
| Thermostat Display | Digital with °F/°C selection |
| Overheat Protection | Automatic shut-off system |
| Housing Material and Waterproof Rating | Stainless steel with IPX4 splash-proof |
Unboxing the LHUKSGF Greenhouse Heater felt like opening a compact, sturdy device designed for serious winter resilience. Its stainless steel housing feels solid in your hand, and the IP X4 waterproof splash proof finish hints at durability.
I immediately noticed the digital thermostat, which is easy to read and switch between °F and °C with just a few taps.
Setting it up was a breeze. The handle and non-slip base make it effortless to move around, whether you’re shifting it in your greenhouse or garage.
I appreciated how lightweight yet stable it felt. The heater heats up quickly, and within minutes, I noticed the ambient temperature rising smoothly and evenly.
The digital thermostat is a game-changer. You can precisely set your desired temperature between 40°F and 108°F, and it automatically turns off once the room reaches that point.
I tested it in a small grow tent, and it maintained a steady climate without any fuss. The overheat protection kicked in once, preventing any risk of damage, and the heater restarted cleanly after cooling down.
During extended use, I found the airflow outlet efficiently circulated warm air, helping my plants stay cozy even during cold snaps. The 5118 BTU/1500W output is just right for spaces up to 150 sq ft.
Plus, the energy-efficient design means I don’t have to worry about sky-high electricity bills.
Overall, this heater feels reliable, straightforward, and built to last. It’s perfect if you want a hassle-free way to keep your plants thriving in winter without overcomplicating things.
What Are the Best Types of Greenhouse Heating Systems Available?
The best greenhouse heating systems vary based on efficiency, cost, and suitability for different types of plants.
- Natural Gas Heaters: These heaters are popular for their efficiency and ability to deliver consistent heat. They are generally less expensive to operate compared to electric systems, making them a cost-effective option for larger greenhouses.
- Electric Heaters: Electric heaters are easy to install and operate, making them ideal for small greenhouses or starter setups. They provide precise temperature control but can be more expensive to run over time, especially in areas with high electricity rates.
- Propane Heaters: Propane heaters offer flexibility and portability, which can be advantageous for mobile greenhouses or those not permanently installed. They produce high heat output quickly but require storage tanks and can incur higher fuel costs compared to natural gas.
- Hydronic Heating Systems: These systems use hot water circulated through pipes to heat the greenhouse, providing even and efficient heat distribution. Though initial installation can be costly, hydronic systems are energy-efficient and can be paired with renewable energy sources, such as solar panels.
- Wood Stoves: Wood stoves are a more traditional option and can be a sustainable choice if you have access to a renewable wood supply. They require regular maintenance and monitoring but can provide an aesthetic and cozy element to the greenhouse environment.
- Heat Mats: Ideal for seed starting and propagating plants, heat mats provide bottom heat to soil, promoting faster germination and growth. They are energy-efficient and can be easily placed under pots or trays, but they may not be suitable for heating large areas.
- Infrared Heaters: Infrared heaters warm objects and plants directly rather than the air, making them efficient for targeted heating in specific areas of the greenhouse. They are great for larger spaces where you want to minimize heating costs, but they may require strategic placement for maximum effectiveness.
How Does Electric Heating Stand Out in Greenhouses?
Electric heating is a popular choice for greenhouses due to its efficiency and control over temperature management.
- Energy Efficiency: Electric heaters convert nearly all their energy into heat, making them highly efficient compared to other systems. This efficiency reduces energy costs, especially in smaller greenhouses where heat loss can be minimized.
- Precise Temperature Control: Electric heating systems allow for accurate temperature settings, which is essential for the optimal growth of plants. Growers can set specific temperatures and maintain consistent conditions, preventing stress on sensitive plants.
- Easy Installation: Electric heating systems are generally easier to install than gas or hydronic systems, as they require minimal infrastructure. This makes them a great option for beginners or those looking to retrofit existing greenhouses.
- Low Maintenance: These systems typically require less maintenance compared to other heating options, as there are no fuel lines, tanks, or complex boiler systems to manage. This reliability makes electric heaters an attractive choice for greenhouse operators.
- Environmental Impact: When powered by renewable energy sources, electric heating can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of greenhouse operations. This aligns with sustainable practices and can appeal to environmentally conscious growers.
- Zoning Capabilities: Electric heaters can be installed in zones throughout the greenhouse, allowing for targeted heating where it is needed most. This zoning helps to optimize energy use and create microclimates for different plant species.
What Are the Key Benefits of Using Gas Heating in Greenhouses?
The key benefits of using gas heating in greenhouses include efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and environmental stability.
- Efficiency: Gas heating systems provide rapid heating, allowing greenhouses to reach desired temperatures quickly. This is particularly beneficial during cold spells when plants require immediate warmth to thrive. Additionally, gas heaters can maintain consistent temperatures, which is crucial for plant growth.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While the initial investment in gas heating may be higher compared to electric systems, gas is often cheaper in the long run. This cost efficiency is due to lower fuel prices and the ability to heat larger spaces without incurring high electricity costs. Greenhouse operators can save money on their energy bills, making it a more economical choice over time.
- Environmental Stability: Gas heating systems can be designed to operate independently of the electrical grid, providing stability during outages. This ensures that plants are not subjected to temperature fluctuations that could damage them. Moreover, modern gas heaters are designed to be more environmentally friendly with lower emissions, contributing to a sustainable greenhouse operation.
- Flexibility: Gas heating systems can be integrated with various greenhouse setups, regardless of size or design. They can also support additional systems such as ventilation and humidity control, creating a comprehensive climate management approach. This adaptability allows growers to customize their greenhouse environment to meet specific crop needs.
- Reduced Maintenance: Gas heating systems typically require less maintenance than electric systems, as they have fewer components that can fail. Regular checks and cleaning are usually sufficient to keep them running smoothly. This reliability means less downtime and more consistent temperatures for the plants.
How Do I Choose the Right Greenhouse Heating System for My Needs?
Choosing the right greenhouse heating system involves considering your specific needs, budget, and climate.
- Natural Gas Heaters: These are efficient and cost-effective for larger greenhouses, providing consistent heat. They typically require proper ventilation and a gas line installation, making them ideal for permanent setups where long-term heating is necessary.
- Electric Heaters: Electric heaters are convenient and easy to install, suitable for smaller greenhouses or those requiring supplemental heating. They come in various sizes, providing flexibility, but can lead to higher electricity bills in large setups.
- Propane Heaters: Propane heaters are portable and can deliver powerful heat quickly, making them a great option for temporary greenhouses or during cold snaps. However, they require a propane tank and regular refills, which can add to ongoing costs.
- Infrared Heaters: Infrared heaters warm objects directly rather than the air, making them efficient for localized heating. They work well in greenhouses with specific temperature zones but may not be suitable for larger spaces without additional heat sources.
- Hot Water Systems: These systems circulate heated water through pipes in the greenhouse, providing a gentle and even heat. They can be energy efficient and are often used in larger setups, but installation can be complex and costly upfront.
- Wood Stoves: Using a wood stove can be an eco-friendly option for heating, especially in rural areas where wood is readily available. While they can be effective and offer a rustic charm, they require regular maintenance and proper ventilation to ensure safety.
- Heat Mats: Ideal for seed starting and delicate plants, heat mats provide gentle bottom heat to promote germination. They are energy-efficient and easy to use but may not suffice for heating an entire greenhouse during extreme cold.
What Factors Influence the Size and Type of Greenhouse Heater I Need?
Several factors influence the size and type of greenhouse heater you need for optimal performance.
- Greenhouse Size: The larger the greenhouse, the more heat is required to maintain an optimal temperature. It’s essential to calculate the total volume of the space to determine the heating capacity needed, which is usually measured in BTUs (British Thermal Units).
- Climate Zone: The local climate significantly affects heating requirements. In colder regions, you may need a more powerful heater or a supplemental heating system, while milder climates might only require minimal heating.
- Plants Being Grown: Different plants have varying temperature needs. For instance, tropical plants thrive in warmer conditions, necessitating a more robust heating system compared to hardy plants that can tolerate cooler temperatures.
- Insulation and Glazing: The materials used for greenhouse walls and roofs can influence heat retention. Well-insulated structures or those with double glazing will retain heat better, potentially reducing the size of the heater needed.
- Heating Method: The type of heating system you choose, such as electric, gas, or propane, will impact the efficiency and overall size requirements. Some methods provide faster heating or more even temperature distribution, which can affect the heater’s sizing.
- Budget: Your budget will determine not only the initial investment in a heating system but also the long-term operational costs. More efficient systems may have a higher upfront cost but can save money over time through reduced energy bills.
- Ventilation Needs: Proper ventilation is crucial in a greenhouse, especially when using heaters. The heater’s size may need to be adjusted based on how much heat will be lost through ventilation systems, which are necessary to regulate humidity and prevent overheating.
How Does Location and Climate Affect My Heating System Choice?
The choice of the best greenhouse heating system is significantly influenced by location and climate conditions.
- Geographic Location: The specific geographical area where the greenhouse is located can determine the heating demands based on regional temperature averages and seasonal variability.
- Climate Zone: Different climate zones, such as temperate, tropical, or arid, require varying heating solutions to maintain optimal growing conditions.
- Insulation Quality: The effectiveness of greenhouse insulation can affect heat retention, thus influencing the type of heating system needed to compensate for heat loss.
- Energy Sources Availability: The availability of various energy sources, such as natural gas, electricity, or biomass, can limit or expand the options for heating systems.
- Humidity Levels: High humidity can affect heating choices since some systems may not perform efficiently or could exacerbate moisture issues.
Geographic location plays a crucial role in selecting a heating system because it dictates the minimum and maximum temperatures that need to be maintained throughout the year. For instance, greenhouses in colder regions may require more robust heating solutions, such as radiant heating or forced air systems, to combat extreme lows.
Climate zones further refine these choices, as a tropical climate may favor less intensive heating methods, such as passive solar heating or lower-capacity electric heaters, while arid zones might require systems capable of managing both temperature and humidity effectively.
Insulation quality is another critical factor; well-insulated greenhouses can retain heat more effectively, potentially allowing for the use of lighter heating systems, while poorly insulated structures may necessitate more powerful units to maintain a stable internal environment.
The availability of energy sources can also dictate the feasibility of certain heating systems. For example, if natural gas is readily available, gas heaters may be the most economical choice, whereas solar heating systems might be preferable in regions with abundant sunlight.
Finally, humidity levels within the greenhouse can complicate heating system selection. Systems that generate excessive heat or dry air might worsen humidity issues, making it essential to choose a system that balances temperature control with moisture management.
What Are the Main Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Greenhouse Heating Option?
| Heating Option | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Heaters | Easy to install, precise temperature control, limited range. | High energy costs, may require electrical upgrades, can be less effective in very large greenhouses. |
| Gas Heaters | Efficient heating, lower operating costs compared to electric. | Requires ventilation, potential safety hazards, dependence on gas supply, emissions may be a concern. |
| Wood Stoves | Low fuel cost, can use renewable resources. | Labor-intensive, requires storage space for wood, smoke and emissions can affect air quality, not suitable for all locations. |
| Hydronic Heating | Even heat distribution, energy-efficient. | High initial installation cost, complex setup, slower to heat up, requires maintenance of boiler system. |
What Are the Unique Pros and Cons of Electric Heating Systems?
| Aspect | Electric Heating Systems |
|---|---|
| Pros | Efficient energy use, lower operating costs, easy installation, environmental benefits with renewable sources, and generally low maintenance requirements. |
| Cons | Higher upfront costs, potential issues with power outages, limited effectiveness in extremely cold climates, safety considerations regarding electrical components, and dependency on electricity availability. |
Why Choose Gas Heating Over Electric Heating for Your Greenhouse?
Choosing gas heating over electric heating for greenhouses often stems from gas systems providing more efficient, cost-effective, and reliable heating solutions, especially in larger spaces.
According to the U.S. Department of Energy, natural gas heating systems can offer significant cost savings compared to electric systems, particularly in regions where gas prices are lower than electricity rates. A study published by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory found that gas heaters can achieve higher thermal efficiency, making them a preferred option for growers focusing on operational costs and energy use (NREL, 2021).
The underlying mechanism for this preference lies in the way gas and electric systems generate heat. Gas heaters burn fuel to create heat, which is then circulated through the greenhouse, often resulting in quicker warming times and a more consistent temperature throughout the space. Electric heaters, while easier to install and maintain, typically require more time to heat the same volume of air, leading to higher energy consumption. Additionally, gas systems can be more easily scaled up for larger greenhouses, which is crucial for commercial operations where maintaining optimal growing conditions is essential for crop yield and quality.
Furthermore, gas heating systems are less susceptible to fluctuations in electricity supply and can operate independently of the grid. This reliability is critical for greenhouse operations, which depend on consistent temperature control to ensure plant health. Electric heating systems may not perform well during power outages or extreme weather conditions, potentially jeopardizing the entire growing cycle. Therefore, many greenhouse operators opt for gas heating to mitigate these risks while maximizing efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
How Can I Improve the Efficiency of My Chosen Greenhouse Heating System?
Improving the efficiency of your greenhouse heating system can significantly enhance plant growth and reduce energy costs. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Insulation: Proper insulation helps to retain heat within the greenhouse, reducing the amount of energy required to maintain optimal temperatures.
- Thermal Mass: Utilizing materials that absorb and store heat, such as water barrels or concrete, can help stabilize temperature fluctuations and provide warmth during cooler periods.
- Efficient Heating Systems: Choosing the best greenhouse heating system, like radiant heaters or biomass boilers, can lead to more effective heat distribution and lower fuel costs.
- Automated Climate Control: Implementing a smart climate control system can optimize heating based on real-time temperature readings, ensuring energy is not wasted.
- Solar Heating: Incorporating solar panels or passive solar design can harness sunlight to heat the greenhouse naturally, thereby reducing reliance on traditional heating methods.
Insulation is critical as it minimizes heat loss, allowing the greenhouse to maintain a stable temperature with less energy consumption. Consider using double-layer polyethylene or thermal curtains to enhance insulation performance.
Thermal mass refers to the capacity of materials to absorb and retain heat. By placing water barrels or stones in the greenhouse, you can capture heat during the day and release it at night, effectively moderating temperature swings.
When selecting an efficient heating system, consider options like radiant heating, which warms plants directly, or biomass boilers that utilize organic materials for a sustainable heat source. These systems can be more cost-effective in the long run compared to traditional electric or gas heating.
Automated climate control systems use sensors and thermostats to monitor greenhouse conditions and adjust heating accordingly. This technology ensures that energy is used wisely, only heating when necessary, which can significantly lower operational costs.
Solar heating can be an eco-friendly alternative, utilizing solar panels to provide energy for heating or leveraging passive solar design elements, such as strategically placed windows, to maximize sunlight exposure and heat retention, further reducing heating costs.
What Are the Best Practices for Optimizing Greenhouse Heating Performance?
The best practices for optimizing greenhouse heating performance involve a combination of system choice, insulation, and management techniques.
- Choose an Efficient Heating System: Selecting the best greenhouse heating system depends on factors such as greenhouse size, plant types, and local climate. Options include gas, electric, and hydronic systems, each with its own efficiency ratings and environmental impacts, so it’s essential to evaluate which system aligns best with your specific needs.
- Insulate the Greenhouse: Proper insulation can significantly reduce heating costs and improve temperature stability. Using thermal screens, double glazing, or insulating materials for walls and roofs helps retain heat more effectively, making the heating system work less and operate more efficiently.
- Implement Zone Heating: Dividing the greenhouse into zones allows for targeted heating, reducing energy waste. By using thermostats to control temperatures in different sections based on plant requirements, you can maintain optimal growing conditions while minimizing energy consumption.
- Utilize Heat Recovery Systems: Incorporating heat recovery systems can capture and reuse waste heat from other processes in the greenhouse. This practice not only improves energy efficiency but also lowers overall heating costs by repurposing heat that would otherwise be released into the atmosphere.
- Monitor and Control Temperature: Installing automated heating controls and sensors can help maintain consistent temperatures, reacting to changes in weather conditions. This ensures the greenhouse remains within the optimal temperature range for plant growth, reducing the workload on heating systems and conserving energy.
- Incorporate Passive Solar Heating: Designing the greenhouse for maximum solar gain can significantly enhance heating performance. Using south-facing windows and thermal mass materials helps absorb and retain heat from sunlight, allowing for reduced reliance on artificial heating sources during sunny days.
- Regular Maintenance of Heating Equipment: Ensuring that heating systems are well-maintained can prevent inefficiencies and breakdowns. Regular checks, cleaning, and servicing of equipment help maintain optimal performance, prolong the life of the system, and ensure that it operates at the highest efficiency level.
How Important Is Insulation in Maximizing Heating Efficiency?
Insulation plays a crucial role in maximizing heating efficiency for greenhouse systems.
- Thermal Mass: Thermal mass refers to materials that absorb and store heat, helping to stabilize temperature fluctuations in a greenhouse. By using materials like concrete or water, heat can be retained during the day and released at night, reducing the need for additional heating.
- Insulated Glazing: Insulated glazing involves using double or triple-pane glass that minimizes heat loss while allowing sunlight to enter. This type of glass creates an air or gas-filled space between panes, which significantly reduces thermal conductivity and enhances overall heating efficiency.
- Sealing and Weatherproofing: Proper sealing around doors, windows, and vents prevents cold air from infiltrating the greenhouse. Weatherproofing ensures that warm air remains inside, which is essential for maintaining a stable and comfortable environment for plants.
- Reflective Materials: Incorporating reflective materials in the design of a greenhouse can direct sunlight towards plants and reduce the need for artificial heating. Reflective surfaces, like mylar or aluminum foil, can enhance light distribution and maximize solar gain, contributing to a more efficient heating system.
- Insulation Materials: Using materials such as foam board, fiberglass, or bubble wrap can significantly reduce heat loss through walls and roofs. These materials have varying R-values, indicating their insulating effectiveness, and selecting the right type can lead to substantial energy savings in heating costs.